Importance of Tracking Denver Temperature
As cities across the globe grapple with climate change, monitoring temperature trends in Denver has become increasingly crucial. Understanding these fluctuations aids in urban planning, environmental conservation, and public health initiatives. Recent reports show that Denver’s temperature is not just vital for its residents but also offers insights into broader climate patterns affecting the western United States.
Recent Temperature Data
According to the National Weather Service, Denver has experienced a notable rise in average temperatures over the past decades. The average annual temperature between 2000 and 2022 was around 50.3°F (10.2°C), a stark increase compared to the 47.8°F (8.8°C) recorded in the 1970s. In 2023, temperatures have continued to reflect this upward trend, with instances of reaching as high as 100°F (37.8°C) during the summer months.
In addition, the Herbert Hoover Drought Index has classified Denver as being in a state of ‘mild drought’ intermittently throughout the mid-year. This dry condition can exacerbate the heat, affecting local water supplies, agriculture, and daily life.
Seasonal Variations and Weather Patterns
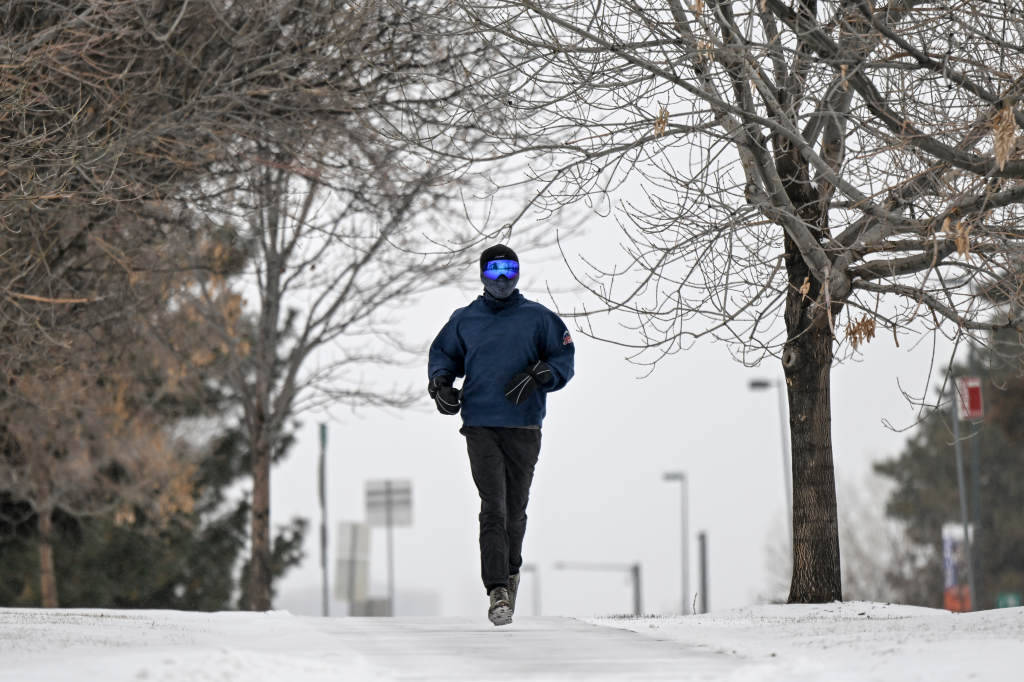
Denver experiences a semi-arid climate, which naturally leads to variability in temperatures. The seasonal changes, from the cold winters to the hot, dry summers, have been more pronounced in recent years, with erratic weather patterns becoming common. For instance, the winter of 2022-2023 featured both record snowfall and sudden warm spells, causing unusual ups and downs in temperatures. Moreover, late-season snowstorms have not been unusual, offering a stark contrast to the preceding warm April days.
Consequences of Temperature Changes
The implications of these temperature shifts reach far beyond discomfort. Public health officials warn that higher temperatures can lead to an increase in heat-related illnesses, particularly among vulnerable populations like the elderly and individuals with chronic illnesses. Urban heat islands, areas in cities that experience higher temperatures due to human activities, pose another risk, leading to increased energy consumption and air pollution.
Conclusion
As Denver continues to navigate the challenges of rising temperatures, it is critical for residents and policymakers to adapt to these changes. Investment in green infrastructure, water conservation strategies, and public education on the impacts of climate change will be essential to mitigating the effects of fluctuating temperatures. Looking ahead, focusing on sustainable practices and effective urban planning can help ensure a livable environment for future generations, even as Denver faces increasing variability in its temperature patterns.