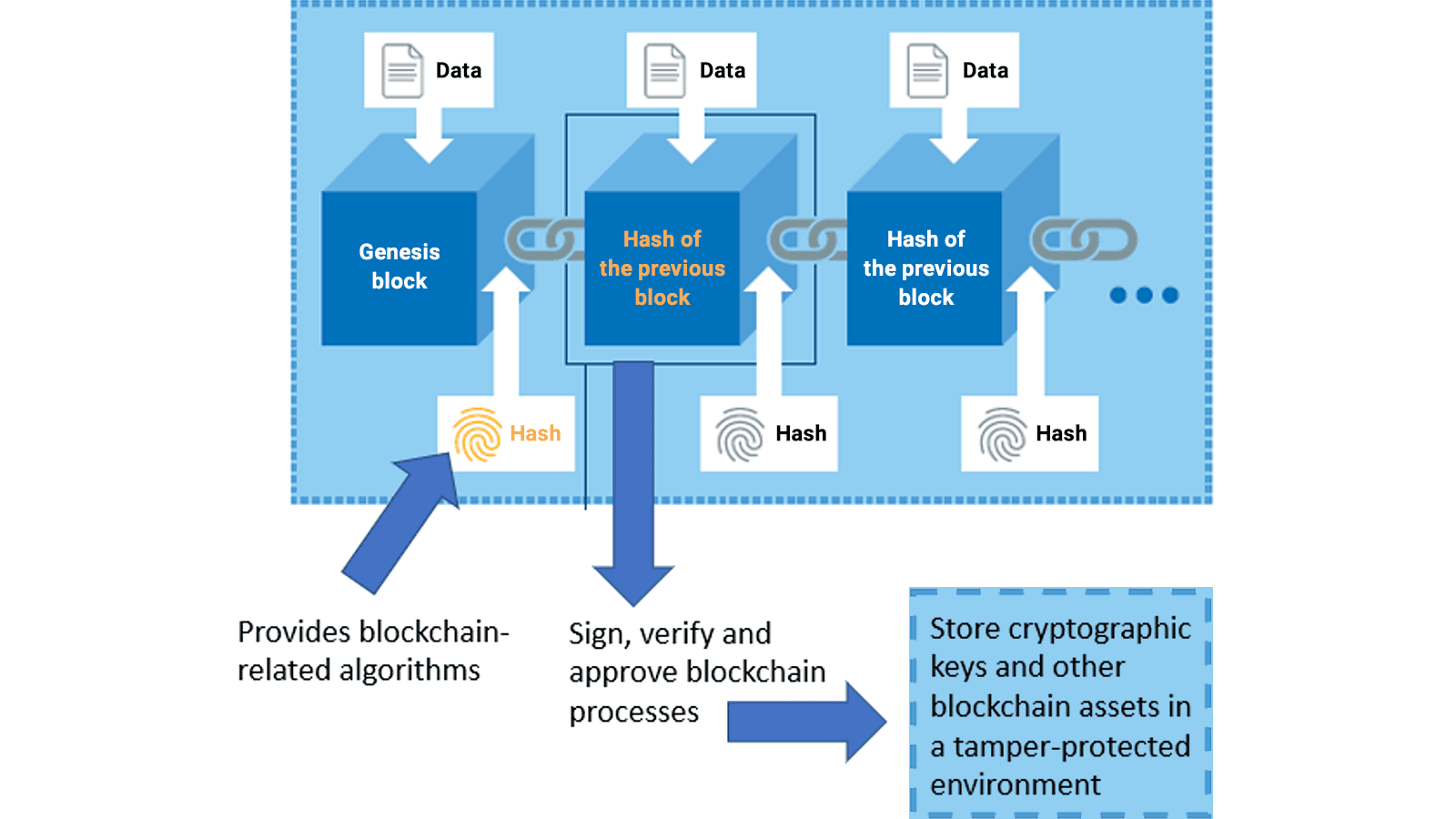
Introduction to Blockchain Applications
In recent years, blockchain technology has emerged as a pivotal influence across various industries, bringing innovation and efficiency to an array of applications. Its decentralized nature, transparency, and security features have made it a game-changer, particularly in sectors such as finance, healthcare, supply chain, and more. The relevance of blockchain applications continues to grow as businesses look for ways to enhance trust and reduce fraud.
Key Blockchain Applications
1. Finance and Payments: One of the most prominent applications of blockchain technology is in the financial sector, particularly for cryptocurrency transactions. Blockchain enables fast, secure peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks, thereby reducing fees and improving transaction speeds. Companies like Ripple and Stellar are spearheading solutions aimed at facilitating cross-border payments.
2. Healthcare: In healthcare, blockchain technology is being adopted for secure health data management. By leveraging a shared, decentralized ledger, patient records can be stored securely and accessed only by authorized personnel, enhancing privacy and security while providing patients with greater control over their data. Projects like MedRec are exploring how this can be implemented effectively.
3. Supply Chain Management: Firms are increasingly utilising blockchain to enhance transparency in supply chains. By allowing all parties to access the same immutable record of transactions, businesses can track products from the manufacturer to the retailer, significantly reducing fraud and ensuring product authenticity. IBM’s Food Trust and VeChain are notable examples that are transforming food safety and supply chain logistics.
4. Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written into code on the blockchain. This application is gaining traction in real estate and legal industries, where it can automate and facilitate transactions, reducing the need for mediators. Ethereum has become a leader in this space, offering developers a platform to build decentralised applications (dApps).
Future Outlook
As the adoption of blockchain technology continues to expand, industries are expected to explore innovative use cases. For instance, in government, blockchain may streamline processes such as voting, preventing fraud and enhancing public trust. In the energy sector, blockchain could be used for decentralised energy trading, allowing consumers to trade surplus energy generated from renewable sources.
Conclusion
The continued development and integration of blockchain applications are likely to lead to significant transformations across various sectors. As more businesses recognise the advantages of blockchain technology, its potential is vast, promising an era of enhanced security, efficiency, and transparency. For businesses and individuals alike, staying informed about these innovations will be crucial in navigating an increasingly digital future.