Introduction
The Ebola virus disease (EVD), a severe and often deadly illness, continues to pose significant challenges to global health. Despite prior outbreaks being largely contained, the emergence of new cases or outbreaks in West and Central Africa remains a critical concern, necessitating ongoing research, vaccination efforts, and public health preparedness. As the world grapples with the COVID-19 pandemic, it is vital to keep an eye on Ebola and other infectious diseases.
Recent Developments
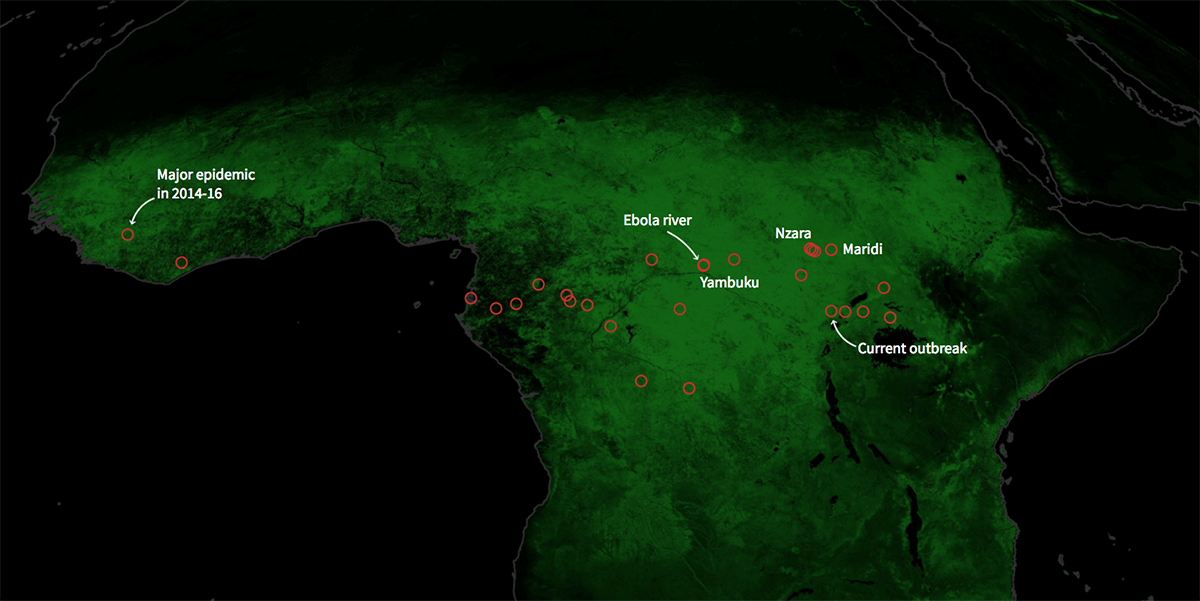
As of late 2023, the World Health Organization (WHO) has reported several new cases of Ebola in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). The latest outbreak, first identified in August 2023, has raised alarms amongst health authorities, with a total of 28 cases reported, including 12 fatalities. This marks the first outbreak in the DRC since 2022, highlighting the endemically public health nature of Ebola in the region.
Vaccination and Response
In response to the surge in cases, the WHO, alongside local health ministries, has mobilised rapid vaccination campaigns utilising the rVSV-ZEBOV vaccine, which has shown efficacy in preventing Ebola infection. Over 10,000 individuals have reportedly been vaccinated in the affected areas since the outbreak was declared. The vaccination drive, although challenging in remote areas, is considered crucial in halting transmission and protecting communities.
Public Health Implications
The recent outbreak underscores the importance of robust healthcare infrastructure and rapid response mechanisms to contain pathogens. Global coordination, including surveillance and research, is essential to prevent a wider spread. Furthermore, the challenge of misinformation regarding disease prevention continues to hinder health efforts in affected areas.
Conclusion
As the global community faces ongoing public health threats, the vigilance towards infectious diseases like Ebola remains paramount. While interventions like vaccination play a critical role, education and awareness are equally important in combating outbreaks. The WHO and other health organizations remain on high alert and continue to emphasise the need for readiness in handling such dangerous diseases. For regional nations and global policy-makers alike, bolstering healthcare systems and fostering international collaboration will be vital in mitigating the impact of future outbreaks.