Introduction
The National Grid plays a crucial role in the energy infrastructure of the United Kingdom. This vast network ensures the reliable distribution of electricity and gas across the country, facilitating essential services and supporting economic growth. As the UK shifts towards greener energy solutions, understanding the National Grid’s importance and its evolving landscape is more relevant than ever.
Current Events and Developments
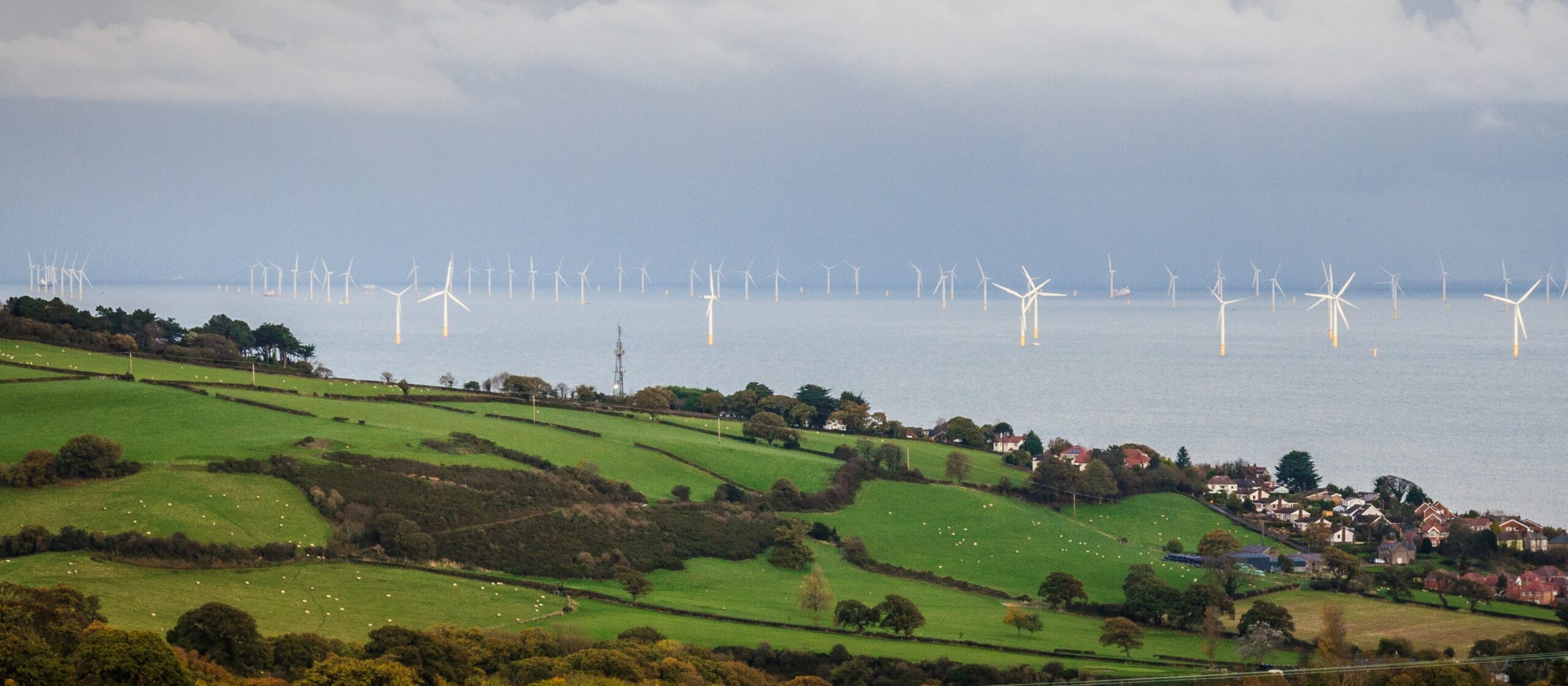
In recent months, the National Grid has faced significant challenges and opportunities. One of the most pressing issues is the increasing demand for electricity, primarily driven by a surge in electric vehicle (EV) usage and the shift to electric heating. This has prompted National Grid to adapt its strategies to ensure that supply can meet future demand. For instance, National Grid Electricity System Operator (ESO) reported that renewable sources like wind and solar now account for 50% of the UK’s electricity generation on certain days, marking a significant milestone in the country’s journey towards net-zero emissions by 2050.
Moreover, with the implementation of policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions, the National Grid is investing in modernising its infrastructure to facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources. This includes enhancing interconnections with neighbouring countries, such as interconnectors to France and the Netherlands, which help to balance electricity supply and demand effectively.
Technological Innovations
Technological advancements are also shaping the future of the National Grid. Smart grid technologies, which allow for improved demand-response capabilities, are being rolled out to better manage the fluctuating supply from renewable sources. These innovations help consumers actively participate in energy management, promoting energy savings and efficiency.
Conclusion
The National Grid is at the forefront of the UK’s energy transition, playing a pivotal role in achieving sustainability goals. As the demand for cleaner energy continues to rise, the importance of a resilient and adaptable National Grid cannot be overstated. Stakeholders, from government bodies to consumers, must stay informed about these developments to ensure a reliable and sustainable energy future. Looking ahead, we can expect further advancements and policies aimed at refining how the National Grid operates, making it a central element in the UK’s pathway to achieving its climate targets.