Introduction to Sudden Stratospheric Warming
Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW) is a significant atmospheric event that occurs when the temperature in the stratosphere, particularly over the polar regions, experiences a rapid increase. This phenomenon can have profound effects on weather patterns, particularly in the Northern Hemisphere, influencing winter weather conditions across Europe, North America, and Asia. With climate change altering weather dynamics globally, understanding SSW has become increasingly important for scientists and meteorologists.
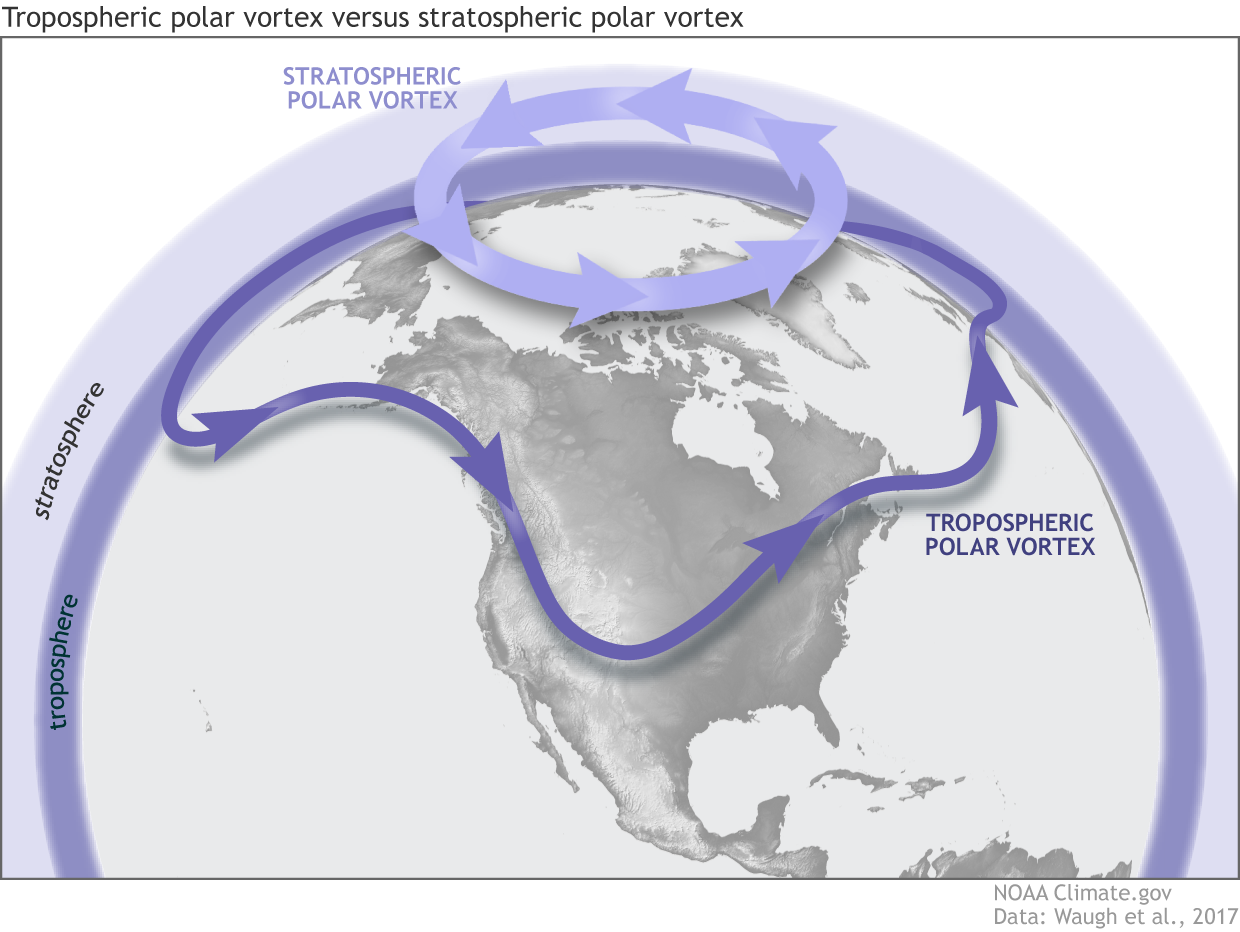
Understanding the Mechanics of SSW
During a typical winter, cold air is trapped over the Arctic by a strong polar vortex. However, during sudden stratospheric warming events, this vortex can become disrupted or weakened due to various factors, including wave interactions from the troposphere. As a result, warm air floods the stratosphere, leading to significant shifts in atmospheric circulation patterns.
Recent studies have highlighted that SSW events can lead to an increase in cold Arctic air spilling southward, which can contribute to extreme cold outbreaks in mid-latitude regions, resulting in heavy snowfall, freezing temperatures, and unusual weather anomalies. For instance, during the SSW event in early 2021, parts of the United States experienced record low temperatures and snowfall, demonstrating the direct connection between these warming events and severe winter weather.
Recent Developments and Findings
According to the latest reports from the Met Office and various climate research institutes, the frequency and intensity of Sudden Stratospheric Warmings are being closely monitored as they appear to be influenced by climate change. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has noted that the warming of the Arctic region may boost the occurrence of SSW events.
Climate researchers are actively studying the implications of SSW on long-term weather patterns. The connection between SSW events and extreme weather phenomena highlights the need for advanced predictive models that incorporate these stratospheric changes, which could aid in better forecasting and preparedness for natural disasters linked with severe winter weather.
Conclusion and Future Implications
In summary, Sudden Stratospheric Warming is a crucial atmospheric phenomenon with significant implications for winter weather patterns across the Northern Hemisphere. As climate change continues to impact global weather systems, the study of SSW becomes essential in understanding and mitigating the effects of extreme weather events. Enhanced awareness and research into SSW can lead to improved forecasting and preparedness, providing key insights into the interconnected nature of our planet’s climate system.